We'll explore how cross-chain interoperability protocols work to solve these challenges by enabling communication and asset exchange between different blockchain networks. This guide compares two leading solutions - Polkadot and Cosmos - examining their approaches to creating an interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
The need for connected blockchains
The blockchain ecosystem currently consists of over 6,500 projects, each operating on independent platforms with unique protocols, consensus methods, and privacy measures. This fragmentation has created a pressing need for connected blockchain networks that can communicate seamlessly.

Current blockchain limitations
Most blockchain networks function as isolated systems, unable to validate data from other chains or external sources. Additionally, each blockchain optimizes specific features while trading off others, making it impossible for a single chain to excel in all aspects. Furthermore, the absence of common standards between different networks has led to a 'state of disorder' in the blockchain ecosystem.
Benefits of interoperability
Blockchain interoperability brings several significant advantages to the ecosystem. First, it enhances liquidity by enabling efficient token movement across different chains. Moreover, it allows users to interact with decentralized finance (DeFi) applications on various blockchains without purchasing native cryptocurrencies.

Cross-chain compatibility significantly improves scalability and user experience. When blockchains can communicate, users gain access to:
- Enhanced functionality through combined features of multiple networks
- Increased flexibility in choosing appropriate tools and platforms
- Simplified token management across various blockchain environments
Key challenges to solve
Nevertheless, achieving seamless blockchain interoperability presents several technical hurdles. Primarily, cross-chain solutions must address scalability issues without compromising speed and efficiency. Subsequently, the complexity of developing and maintaining interoperability protocols demands substantial resources.
Security remains a critical concern, particularly in cross-chain interactions. The exposure to vulnerabilities increases when previously isolated blockchains begin communicating. Furthermore, different blockchains operate with varying trust models and security levels, making it challenging to maintain consistent security standards across networks.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. Cross-chain solutions must navigate diverse jurisdictional requirements and comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. Additionally, the absence of standardized protocols for cross-chain communication makes it difficult to establish uniform security measures.
Core features of Polkadot
Polkadot stands out as a multi-chain blockchain platform designed to enable seamless message and value transfers across different networks. At its foundation lies two core features that make it uniquely positioned to solve blockchain interoperability challenges.
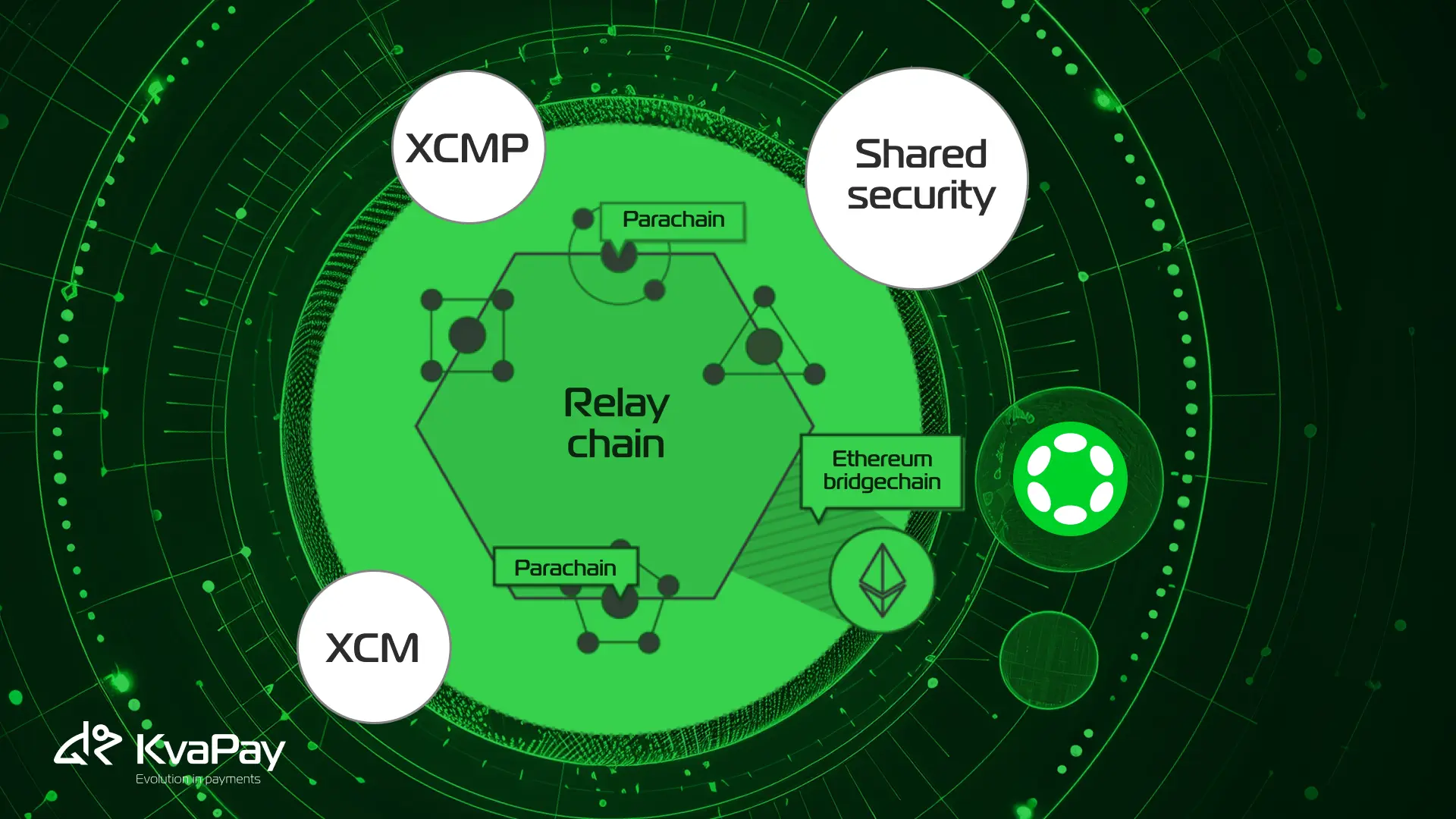
Cross-chain messaging
Cross-Consensus Messaging (XCM) forms the backbone of Polkadot's interoperability solution. Rather than being a protocol, XCM serves as a standardized messaging format that allows different consensus systems to communicate effectively. This framework operates on four key principles: asynchronous, absolute, asymmetric, and agnostic.
Through XCM, blockchains can:
- Transfer tokens and assets between chains
- Share data across networks
- Execute complex cross-chain operations
The actual delivery of these XCM-formatted messages occurs through Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP), the network-layer protocol connecting participating parachains. This system enables multi-hop, multi-network communications while maintaining security and efficiency.
Shared security
One of Polkadot's most distinctive features is its shared security model, which allows multiple blockchains to benefit from the network's established validator set. The Relay Chain acts as the central coordinator, providing shared security and consensus across all connected parachains.
This security framework relies on four key participants:
- Validators: Full-node operators who maintain network consensus and validate blocks on the Relay Chain
- Nominators: Participants who select trustworthy validators by staking DOT
- Collators: Nodes that maintain parachains by collecting transactions
- Fishermen: Security monitors who report malicious behavior
The shared state between the Relay Chain and connected parachains ensures that if the Relay Chain needs to revert, all parachains revert accordingly. This mechanism maintains system-wide validity without compromising individual chain integrity.
How Cosmos works
The Cosmos network introduces a unique approach to blockchain interoperability through its ecosystem of independent yet connected chains. Unlike traditional blockchain architectures, Cosmos employs a modular framework that simplifies blockchain development and enables cross-chain communication.
Independent blockchain zones
Cosmos utilizes specialized zones - independent blockchains designed for specific purposes. These zones maintain their sovereignty yet can communicate seamlessly with other chains in the ecosystem. The network's architecture incorporates three fundamental components:
- Tendermint Core: Handles consensus and networking layers
- Cosmos SDK: Provides pre-written modules for rapid development
- Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol: Enables cross-chain messaging
The IBC protocol has expanded significantly, connecting over 115 networks and serving more than 700 000 monthly active users by the end of 2025.

The role of the Cosmos Hub
At the center of the Cosmos ecosystem lies the Cosmos Hub, a proof-of-stake blockchain that serves as a crucial middleware connecting various zones. The Hub facilitates:
- Secure token transfers between different zones
- Cross-chain validation and consensus
- Coordinated communication between independent blockchains
The Hub operates through validators who maintain network consensus and ensure transaction finality. This architecture enables parallel processing of transactions across multiple chains, enhancing overall system efficiency.
Token transfers between chains
Token transfers within Cosmos occur through a sophisticated process that maintains security and transparency. Upon initiating a transfer, tokens are locked in an escrow address on the source chain. The process follows these steps:
- Transaction commitment on the source chain
- IBC Relayers detect and reconstruct the data package
- Verification through Light Clients on the destination chain
- Token minting on the receiving chain
The IBC protocol employs unique identifiers called "IBC denoms" that track token paths across chains. This system enables seamless transfers without requiring exchange liquidity between zones. Consequently, users can move assets between chains efficiently, opening new possibilities for cross-chain DeFi applications.
Real-world applications
Cross-chain solutions have sparked innovative applications across multiple sectors, fundamentally changing how businesses and users interact with blockchain technology. These practical implementations showcase the true potential of blockchain interoperability.
DeFi use cases
Financial services have emerged as a primary beneficiary of cross-chain functionality. Multi-collateral lending platforms now enable users to borrow assets from one blockchain using collateral from another. Through cross-chain protocols, unified liquidity pools optimize capital efficiency, offering enhanced yield farming opportunities.
THORChain's decentralized exchange supports native asset swaps across chains, establishing deeper markets for efficient price discovery. Similarly, platforms like Aave have introduced cross-chain markets, allowing Bitcoin holders to secure loans in Ethereum-based stablecoins.
Enterprise adoption
For businesses, blockchain interoperability has become essential for maximizing operational efficiency. Companies implementing interoperable solutions have reported up to 80% reduction in transaction costs compared to traditional methods. This dramatic improvement stems from automated recordkeeping and smart contract capabilities.
Major corporations have already begun integrating these solutions:
- Walmart utilizes Hyperledger for cross-network supply chain tracking
- IBM's blockchain platform enables secure data sharing spaces for multi-chain governance
- VeChain implements multi-chain tracking with IoT for real-time asset verification
Cross-chain NFTs
The non-fungible token landscape has undergone substantial transformation through cross-chain capabilities. Cross-chain NFTs can now move freely between multiple blockchain networks while maintaining their authenticity and value. This advancement has created several groundbreaking possibilities:
- Gaming assets that seamlessly transfer across virtual worlds
- NFT composability allowing simultaneous use across different protocols
- Multi-chain auctions enabling broader market exposure
Chainlink's Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) has pioneered secure cross-chain NFT implementations, enabling projects to offer their tokens across multiple blockchains. This innovation allows NFT ownership data to be natively available across chains, simplifying external development and fostering new use cases like cross-chain NFT lending platforms.
Conclusion
Blockchain interoperability stands as a crucial stepping stone toward widespread adoption of decentralized technology. While both Polkadot and Cosmos offer unique approaches to cross-chain communication, their distinct architectures serve different needs within the ecosystem. Polkadot's shared security model and XCM protocol provide robust protection for parachains, therefore making it suitable for security-critical applications. Additionally, Cosmos' independent zones and IBC protocol offer greater flexibility for projects requiring sovereign blockchains.
Real-world implementations across DeFi, enterprise solutions, and NFTs demonstrate the practical value of cross-chain compatibility. These applications prove that interoperability solutions can reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and create new possibilities for blockchain adoption.
Above all, the success of cross-chain solutions depends on their ability to maintain security while enabling seamless communication between networks. As blockchain technology matures, projects like Polkadot and Cosmos will likely continue refining their approaches, bringing us closer to a truly interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Tags:
Share:

