How DORA Regulation Shapes the Future of Cryptocurrency Businesses
31 January 2025
7 min for read
DORA regulation represents a major transformation in cryptocurrency business operations across the European Union. This detailed regulatory framework sets strict operational resilience requirements that will revolutionize the digital asset world. Cryptocurrency platforms now merge more with traditional financial systems, making it crucial to understand DORA regulation's impact on operational processes, risk management strategies, and technology infrastructure.
Our detailed DORA regulation overview shows the broad reach of these new requirements. This piece explores the key compliance elements crypto businesses need, such as ICT risk management protocols, third-party service provider oversight, and incident response planning. Businesses will find practical implementation strategies, timelines, and resource allocation frameworks to adapt to these regulatory changes effectively.
Understanding DORA's Impact on Cryptocurrency Operations
The cryptocurrency sector is experiencing major changes with DORA's introduction of an integrated framework that manages risk from start to finish. This regulation brings several vital changes to how crypto operations work.
Key Requirements for Crypto Businesses
Crypto-asset service providers must put detailed ICT risk management frameworks in place. The key requirements include:
- Establishing information security policies
- Implementing incident detection mechanisms
- Developing ICT business continuity plans
- Creating backup strategies
- Preparing incident communication plans
- Providing mandatory cybersecurity training for staff
Timeline for Implementation
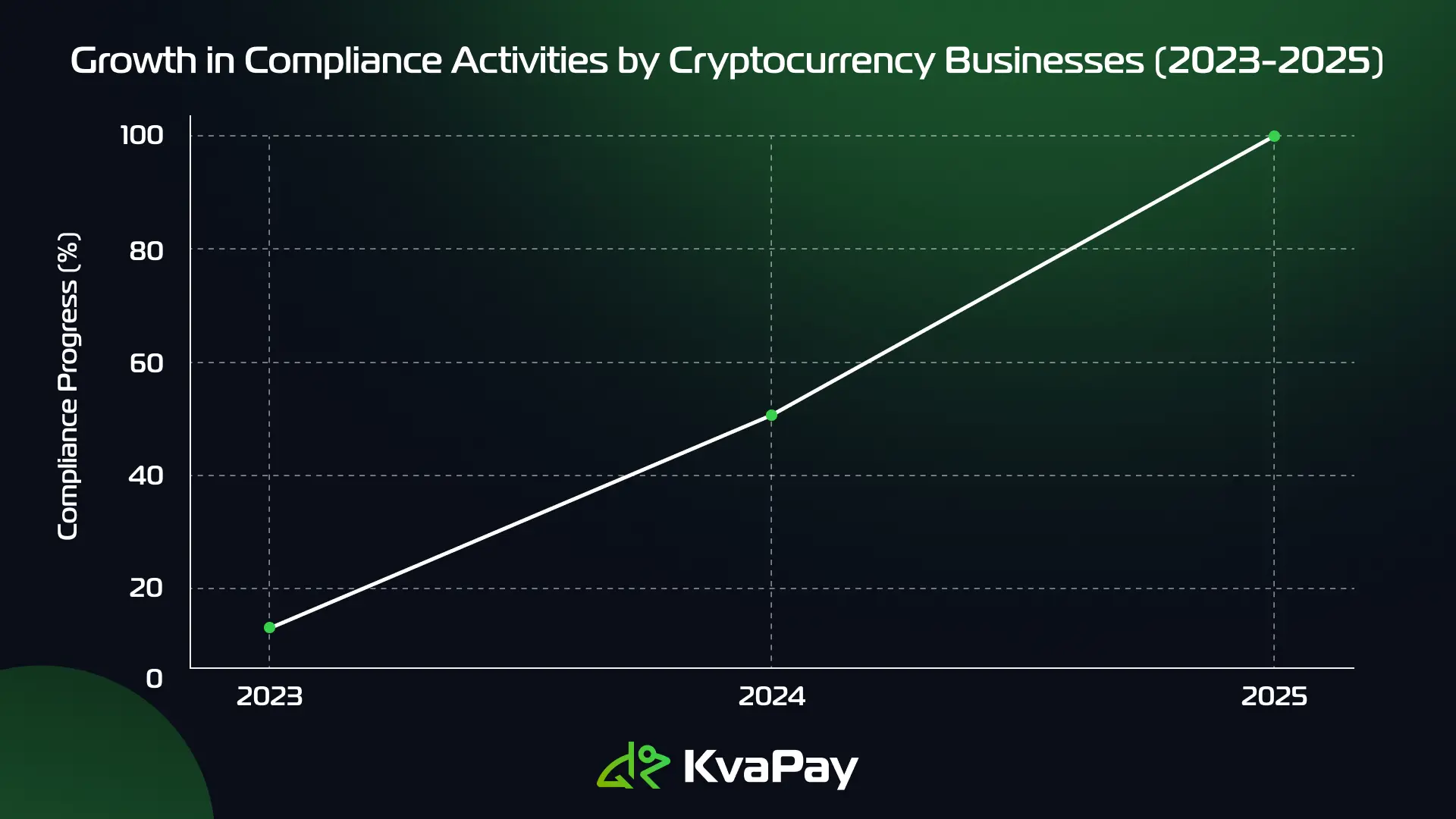
The implementation schedule started at the time DORA came into effect on January 16, 2023. The regulation follows this timeline:
- Entry into Force: January 16, 2023
- Full Compliance Deadline: January 17, 2025
- Implementation Period: Two years for financial entities to achieve compliance
Scope and Jurisdiction
DORA's reach extends beyond traditional financial institutions to include crypto businesses of all types. The regulation applies to:
- Custodial wallet providers
- Cryptocurrency exchanges and trading platforms
- Crypto-asset placement services
- Crypto-asset advisory services
- Portfolio management services
DORA stands out by bringing together ICT risk management requirements that were once spread across different legal acts. Third-party resilience needs close interaction with critical ICT service providers that support vital business services.
The core team must get involved to implement this effectively. They need to appoint dedicated staff who will handle ICT risk management. Regular testing of critical ICT systems is also required. This includes network security assessments, scenario testing, and penetration testing.

Risk Management Framework for Crypto Platforms
The risk management framework implementation under DORA focuses on building a strong structure that tackles unique challenges in cryptocurrency operations. This framework has complete ICT risk management, incident handling, and business continuity planning.
ICT Risk Assessment Protocols
A complete ICT risk management system must be established with detailed threat registers and vulnerability assessments. The framework requires:
- Continuous monitoring of network security
- Regular assessment of information assets
- Assessment of potential vulnerabilities
- Documentation of technical measures
- Implementation of organizational controls
Incident Response Planning
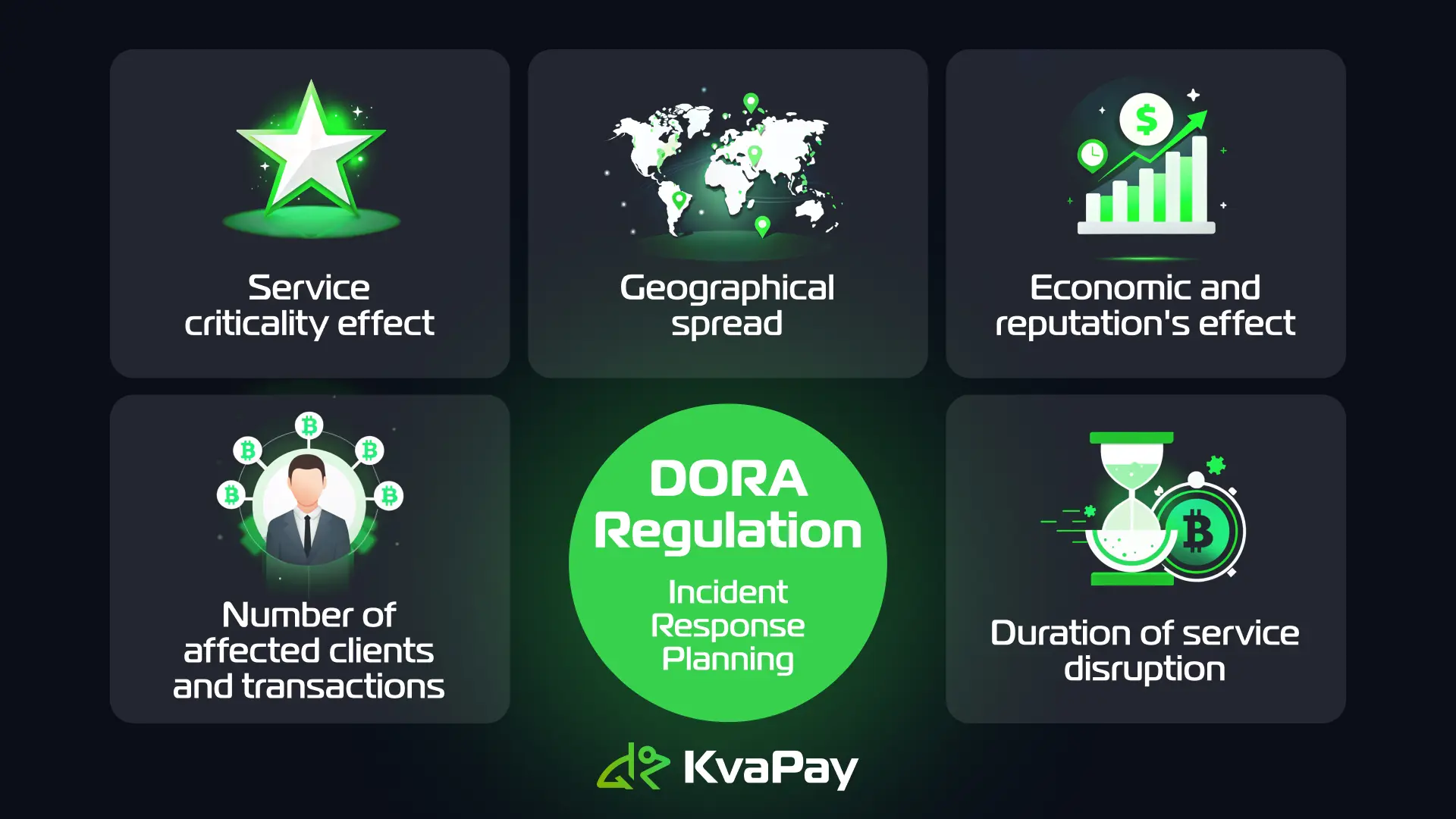
The incident response strategy arranges with DORA's classification criteria to assess incidents based on:
- Service criticality effect
- Number of affected clients and transactions
- Geographical spread
- Duration of service disruption
- Economic and reputation's effect
Critical incidents need three types of reports: original notification, intermediate updates, and final analysis. This well-laid-out approach will give a clear line of communication with regulators and affected parties.
Business Continuity Requirements
Business continuity planning must consider severe but plausible scenarios that could disrupt critical functions. Testing procedures assess:
Recovery Capabilities: Systems must show they can maintain critical functions and restore normal operations quickly.
Infrastructure Resilience: Testing scenarios with switchover from primary ICT infrastructure to redundant facilities is essential.
Communication Protocols: Plans need clear procedures for staff and ICT service provider coordination during incidents.
The management body is vital in overseeing these measures and has specific responsibilities to approve and monitor the ICT risk management framework. Employee awareness programs help maintain strong cyber risk consciousness throughout the organization.

Third-Party Service Provider Management
Our cryptocurrency operations need a complete approach to manage third-party service providers under DORA and ensure operational resilience. The critical framework has several important components we need to break down.
Vendor Assessment Criteria
The vendor assessment process aligns with ESAs' two-step approach to identify critical ICT third-party service providers (CTTPs). Quantitative criteria help create the first selection pool. A detailed qualitative analysis follows to get the full picture. This review process helps us spot providers that need better oversight and stronger risk management.
Contractual Obligations
Our new robust contractual arrangements must cover specific mandatory elements. ICT service contracts now include:
- Clear service descriptions and data processing locations
- Data protection and recovery provisions
- Incident support requirements
- Service level specifications
- Termination rights and notice periods
- Cooperation protocols with authorities
Services that support critical functions need extra contractual elements. This creates different levels of provider management.
Oversight Mechanisms
The European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs) created a new oversight framework for critical providers. This framework affects us in several ways:
Enhanced Monitoring: ESAs can review and inspect critical providers' risk management processes and how they handle governance.
Financial Accountability: Critical ICT third-party service providers face penalties up to 1% of their annual worldwide turnover if they don't comply.
Continuous Assessment: An information register tracks all ICT service contractual arrangements. Regulators must be able to access this documentation by April 30, 2025.
Digital resilience stays our responsibility even when we use external ICT providers. Our third-party systems need the same strict testing as internal systems. This maintains consistent resilience standards throughout our operations.
Compliance Implementation Strategy
Getting ready for DORA compliance needs a well-laid-out approach that will shape our cryptocurrency operations. The challenge lies in managing both DORA and MiCA requirements at the same time.
Gap Analysis Methodology
A full picture of our current cybersecurity practices compared to DORA's compliance requirements forms the foundation of our gap analysis. We have created a systematic evaluation that has:
- ICT infrastructure assessment
- Compliance process documentation
- Risk management framework review
- Security arrangement evaluation
This analysis helps us spot areas that need quick attention and lets us prioritize our compliance work effectively.
Resource Allocation Framework
Three key areas demand substantial investment:
- Technical Infrastructure Updates
- Compliance Process Development
- Specialized Personnel Recruitment
Our strategy aims to build essential knowledge and expertise while distributing the budget across each compliance component. The policies and procedures must meet both MiCA and DORA requirements to complete the application.
Timeline Management
The short transition period creates major challenges for implementation. We need careful coordination since we'll be among the first entities evaluated for DORA compliance during licensing.
Key deadlines shape our timeline strategy:
The technical standards application date of January 17, 2025 drives our focus. We must ensure our systems and processes meet all requirements by then. This includes building strong ICT risk management frameworks and setting up incident reporting systems.
We work closely with regulatory authorities to understand their expectations. Our assessment will create precedents for future applicants. We prepare proactively and monitor legislative changes to stay current with evolving requirements.
Conclusion
DORA regulation brings a major transformation to cryptocurrency businesses operating in the European Union. Our detailed analysis outlines everything you need to know for successful compliance - from complete ICT risk management to oversight of third-party service providers.
Your business needs proper preparation in these key areas to meet DORA requirements:
- Strong ICT risk assessment protocols
- Clear incident response strategies
- Complete business continuity planning
- Full third-party service provider management
- Smart resource allocation
Cryptocurrency businesses must act now as the January 17, 2025 deadline approaches fast. A successful compliance experience requires technical infrastructure updates, process development and recruitment of specialized personnel to work together smoothly.
Your operational resilience must remain strong while adapting to new regulatory standards. This will help you succeed under DORA. Follow KvaPay to learn more tips from the cryptocurrency world! This regulatory framework creates new standards for digital operational resilience that help cryptocurrency businesses become more secure and stable in the European financial ecosystem.
Tags:
Share:

